Git Commands 1
Git is a powerful version control system. This tutorial will guide you through some basic git commands and workflows to help you manage your projects.

Official Git Document: https://git-scm.com/docs/git
Cloning a Repository
To clone (or copy) a repository from a remote source like GitHub:
git clone [repository-url]
Initialize a New Repository
To start a new git repository in a directory:
- Navigate to the directory:
cd [your-folder-name]
- Initialize the repository:
git init
This will create a hidden .git folder in the directory.
Checking the Status
To see the status of files (tracked, untracked, modified):
git status
Tracking and Staging Files
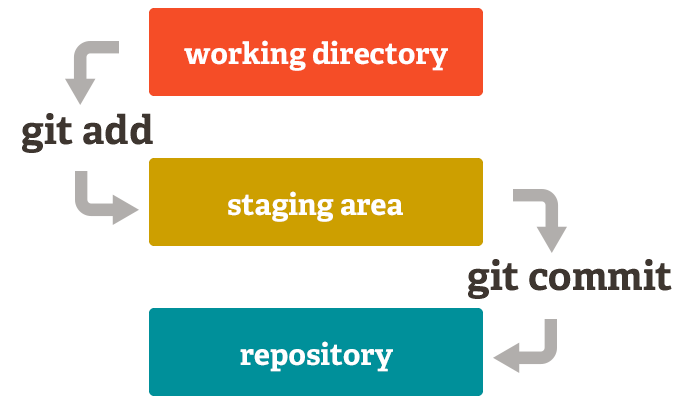
Image source: "Git Gud: The Working Tree, Staging Area, and Local Repo" by Lucas Maurer, Medium, 10 Oct 2017.
To start tracking and staging new or modified files:
- Add a specific file:
git add [file-name]
- Or add all files:
git add --all
or
git add .
Ignoring Files
To ignore certain files or patterns, create a .gitignore file in your repository root. For example, to ignore all .txt files and don't let them be tracked:
# .gitignore
*.txt
Committing Changes
To save the staged changes:
git commit -m "Your commit message here"
Bypass Staging
If you want to bypass the staging area and commit all changes directly:
git commit -a -m "Your commit message here"
Unstaging Files
To remove files from the staging area:
git restore --staged [file-name]
Viewing Commit History
To see the commit history:
git log
For a more concise view:
git log --oneline
Working with Branches

Screenshot from "Loki" Season 2, Episode 2, Marvel Studios, 2023.
Creating a Branch
To create a new branch:
git branch [new-branch-name]
Switching Branches
To switch to another branch:
git switch [branch-name]
To create a new branch and switch to it immediately:
git switch -c [new-branch-name]
Merging Branches
To merge changes from another branch into your current branch:
git merge -m "Your merge commit message here" [branch-name-to-merge]
Deleting a Branch
To delete a branch:
git branch -d [branch-name]
Remote Repositories
Adding a Remote
To link your local repository to a remote repository:
git remote add origin [repository-url-from-github-or-other-platform]
Pushing Changes
To push your local commits to the remote repository:
- Set the main branch (only needs to be done once):
git branch -M main
- Push the changes:
git push -u origin main
Pulling Changes
To fetch and merge changes from the remote repository:
git pull
This tutorial covers the basics of git. There's a lot more to explore, but with these commands, you can effectively manage and collaborate on projects. Happy coding!
Comments
Post a Comment